2.3 TensorFlow Lite端侧学习
2.3.1 简介
2019年12月12日Pavel Senchanka在Google TensorFlow官方blog上提出了一种基于TsnsorFlow Lite实现的端侧模型定制化的文章(Example on-device model personalization with TensorFlow Lite),该文章通过一个TensorFlow Lite demo程序,演示了在移动设备上如何利用已经预先训练好的MobileNet V2模型,通过替换最后几层为softmax分类器形成一个新的模型,然后在移动设备上只训练softmax部分从而达到图像分类的目的,也就是我们常说的端侧迁移学习。
该方案解决了TensorFlow传统方案模型训练所需数据多,计算量大,耗时长的缺点,为移动设备参与训练,学习打开了一个全新的大门,在计算量与效果之间取得了很好的平衡。该演示demo程序充分考虑了移植需求,converter工具和runtime可以很简单的应用到其他类似需求上,非常值得借鉴。
2.3.2 实现方案
Pavel Senchanka方案基于最简单的transfer learning模型,也即fine tune模型。它要求source data(预训练模型用的数据)和dest data(新分类任务数据)都是label过的,且基于如下知识:
- 预先训练好的模型是久经考验的经典模型,训练非常耗时。
- 图像分类模型前面一些layer是提取特征,后面一些layer是分类。
- 图像分类模型替换掉最后面的分类layer,可以transfer learning到不同的分类能力。
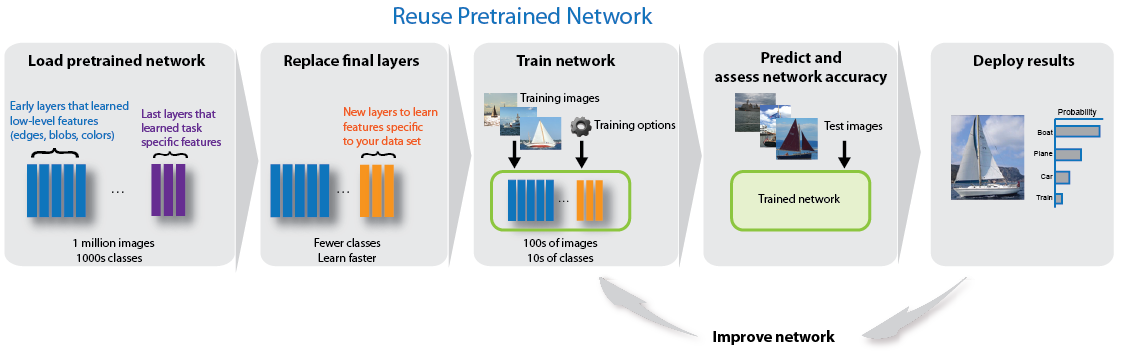
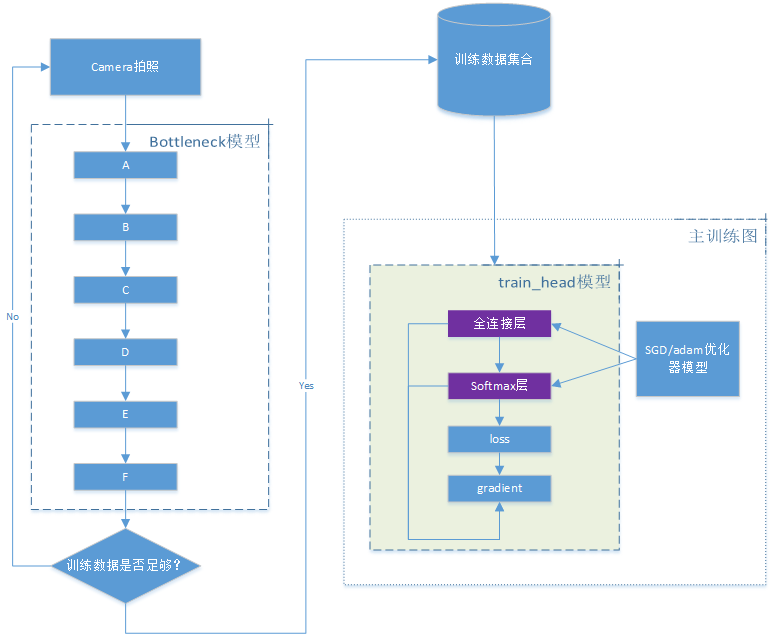
Pavel Senchanka方案系统框架如下图所示:
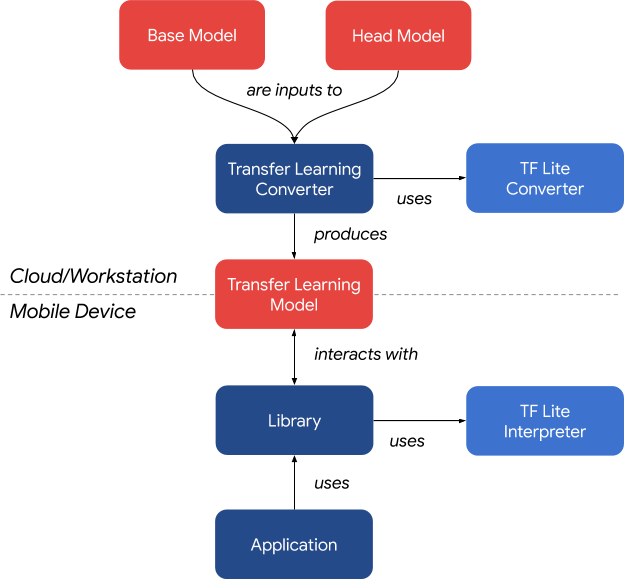
简单来讲,设计分为2部分,以上图虚线为分割:
- 上半部分的核心是Transfer Learning converter这个工具(python实现),它借助TensorFlow Lite converter命令将2个输入base和head模型转换成runtime需要的模型组,即迁移学习模型,完成模型准备工作,该步骤可在云端或者工作站进行。
- 下半部分是应用框架,运行在移动设备上。它的核心是Libray,也就是所谓的runtime,它对上接android应用,对下管理迁移学习模型。
2.3.3 方案分析
2.3.3.1 converter
2.3.3.1.1 依赖
1
2
3
|
tensorflow==2.0.0rc0
Pillow==6.2.0
scipy==1.3.0
|
2.3.3.1.2 参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
usage: tflite_transfer_convert.py [-h] [--train_batch_size TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE]
[--num_classes NUM_CLASSES]
(--base_mobilenetv2 | --base_model_dir BASE_MODEL_DIR)
[--base_quantize]
(--head_model_dir HEAD_MODEL_DIR | --head_softmax)
[--head_l2_reg HEAD_L2_REG] --optimizer
{sgd,adam}
[--sgd_learning_rate SGD_LEARNING_RATE]
--out_model_dir OUT_MODEL_DIR
Combines two TF models into a transfer learning model
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--train_batch_size TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE
Training batch size
--num_classes NUM_CLASSES
Number of classes for the output
--base_mobilenetv2 Use MobileNetV2 as the base model
--base_model_dir BASE_MODEL_DIR
Use a SavedModel under a given path as the base model
--base_quantize Whether the base model should be quantized
--head_model_dir HEAD_MODEL_DIR
Use a SavedModel under a given path as the head model
--head_softmax Use SoftmaxClassifier for the head model
--head_l2_reg HEAD_L2_REG
L2 regularization parameter for SoftmaxClassifier
--optimizer {sgd,adam}
Which optimizer should be used
--sgd_learning_rate SGD_LEARNING_RATE
Learning rate for SGD
--out_model_dir OUT_MODEL_DIR
Where the generated transfer learning model is saved
|
2.3.3.1.3 用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
# Create a virtualenv. This step is optional but recommended.
virtualenv venv
# Activate the created virtualenv.
source venv/bin/activate
# Install the converter.
pip install -e .
# Convert the model.
tflite-transfer-convert \
--base_mobilenetv2 \
--head_softmax \
--num_classes=4 \
--train_batch_size=20 \
--optimizer=sgd \
--sgd_learning_rate=0.0003 \
--out_model_dir=mobilenet_softmax_model
|
converter的主要参数如下表所示:
| 参数 |
含义 |
| base模型 |
预先训练好的模型,支持预设的mobilenet v2模型或者自定义模型,支持量化 |
| head模型 |
新的可训练模型,支持softmax_classifier(全连接层 + softmax激活函数,交叉熵损失函数模型,转换时仅支持tf lite内置算子)或者自定义模型(转换时采用Tensorflow Select Operators提升兼容性,但占用空间大,初始化更耗时) |
| 优化器 |
支持sgd(支持设置学习速率),adam |
| out_model_dir |
输出迁移学习模型目录 |
| train_batch_size |
训练次数 |
| num_classes |
分类个数 |
2.3.3.1.4 转换结果
| 迁移学习模型文件 |
含义 |
| train_head.tflite |
训练模型,执行训练任务,基于Head Model构造,在其后添加了交叉熵损失函数层和梯度计算层。 |
| optimizer.tflite |
优化器模型,输入为当前可训练参数,梯度,优化器状态,输出为新的可训练参数,优化器状态。 |
| bottleneck.tflite |
Bottleneck是base模型前半部分的输出,head模型的输入。 |
| inference.tflite |
推理模型,由head模型构造,它以bottleneck的输出为输入,包含所有可训练的head参数。 |
| initialize.tflite |
模型初始化参数 |
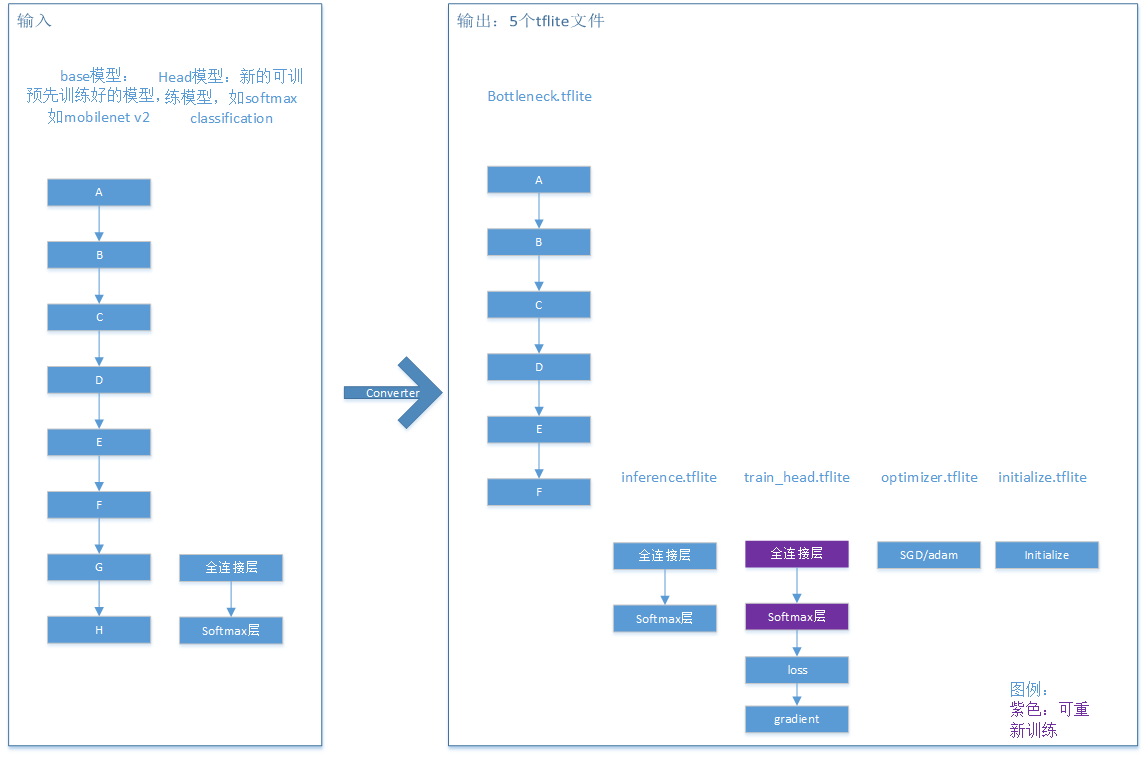
2.3.3.2 应用
普通android应用,调用camera模块获取照片先进行训练,然后就可以执行推理。
应用层很薄,核心是调用runtime AssetModelLoader类的train,predict函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
TransferLearningModelWrapper(Context context) {
model =
new TransferLearningModel(
new AssetModelLoader(context, "model"), Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "4"));
new Thread(() -> {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
shouldTrain.block();
try {
model.train(1, lossConsumer).get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Exception occurred during model training", e.getCause());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// no-op
}
}
}).start();
}
public Prediction[] predict(float[] image) {
return model.predict(image);
}
|
2.3.3.3 runtime
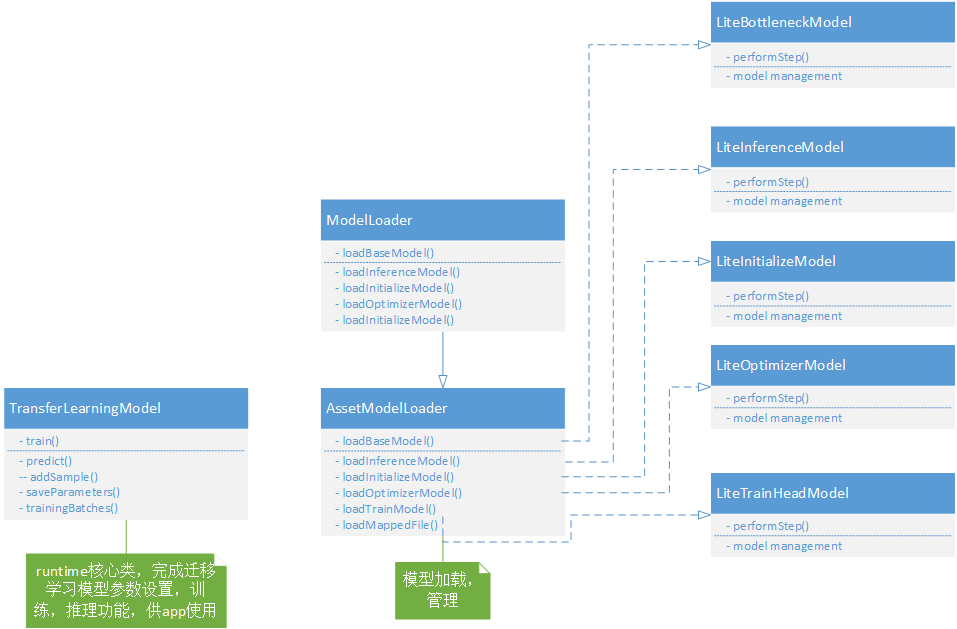
这是一个可复用的gradle模块,目前只实现了android版本,可以很方便地集成在任何一个android应用里。其框架如下图所示,LiteXXXModel的几个类用于加载,管理converter转换出来的迁移学习模型,每个文件对应一个类,AssetModelLoader是对外的接口,可供app使用。TransferLearningModel是runtime的核心,完成迁移学习模型参数设置,训练,推理功能,app一般通过它来同runtime交互实现迁移学习。
训练代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
public Future<Void> train(int numEpochs, LossConsumer lossConsumer) {
checkNotTerminating();
if (trainingSamples.size() < getTrainBatchSize()) {
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format(
"Too few samples to start training: need %d, got %d",
getTrainBatchSize(), trainingSamples.size()));
}
return executor.submit(
() -> {
trainingLock.lock();
try {
epochLoop:
for (int epoch = 0; epoch < numEpochs; epoch++) {
float totalLoss = 0;
int numBatchesProcessed = 0;
for (List<TrainingSample> batch : trainingBatches()) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
break epochLoop;
}
trainingBatchClasses.put(zeroBatchClasses);
trainingBatchClasses.rewind();
zeroBatchClasses.rewind();
for (int sampleIdx = 0; sampleIdx < batch.size(); sampleIdx++) {
TrainingSample sample = batch.get(sampleIdx);
// 训练数据由bottleneck模型计算出来
trainingBatchBottlenecks.put(sample.bottleneck);
sample.bottleneck.rewind();
// Fill trainingBatchClasses with one-hot.
int position =
(sampleIdx * classes.size() + classes.get(sample.className)) * FLOAT_BYTES;
trainingBatchClasses.putFloat(position, 1);
}
trainingBatchBottlenecks.rewind();
// 由trainheadModel计算loss
float loss =
trainHeadModel.calculateGradients(
trainingBatchBottlenecks,
trainingBatchClasses,
modelParameters,
modelGradients);
totalLoss += loss;
numBatchesProcessed++;
// 优化器迭代一次
optimizerModel.performStep(
modelParameters,
modelGradients,
optimizerState,
nextModelParameters,
nextOptimizerState);
ByteBuffer[] swapBufferArray;
// Swap optimizer state with its next version.
swapBufferArray = optimizerState;
optimizerState = nextOptimizerState;
nextOptimizerState = swapBufferArray;
// Swap model parameters with their next versions.
parameterLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
swapBufferArray = modelParameters;
modelParameters = nextModelParameters;
nextModelParameters = swapBufferArray;
} finally {
parameterLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
float avgLoss = totalLoss / numBatchesProcessed;
if (lossConsumer != null) {
lossConsumer.onLoss(epoch, avgLoss);
}
}
return null;
} finally {
trainingLock.unlock();
}
});
}
|
推理代码:由bottleneck模型和inference模型组合计算推理结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public Prediction[] predict(float[] image) {
checkNotTerminating();
inferenceLock.lock();
try {
if (isTerminating) {
return null;
}
// 准备图像数据做推理
ByteBuffer imageBuffer = allocateBuffer(image.length * FLOAT_BYTES);
for (float f : image) {
imageBuffer.putFloat(f);
}
imageBuffer.rewind();
// 计算bottleneck输出
ByteBuffer bottleneck = bottleneckModel.generateBottleneck(imageBuffer, inferenceBottleneck);
float[] confidences;
parameterLock.readLock().lock();
try {
// 由bottleneck计算inference结果
confidences = inferenceModel.runInference(bottleneck, modelParameters);
} finally {
parameterLock.readLock().unlock();
}
// 取得分类结果概率数组
Prediction[] predictions = new Prediction[classes.size()];
for (int classIdx = 0; classIdx < classes.size(); classIdx++) {
predictions[classIdx] = new Prediction(classesByIdx[classIdx], confidences[classIdx]);
}
// 排序输出最大可能结果
Arrays.sort(predictions, (a, b) -> -Float.compare(a.confidence, b.confidence));
return predictions;
} finally {
inferenceLock.unlock();
}
}
|
2.3.4 未来演进
- 未来将会在当前迁移学习实现的基础上实现在TensorFlow Lite上的全训练解决方案。
- 迁移学习模型执行无需调用额外的runtime。
2.3.5 总结
- Pavel Senchanka提出的TensorFlow Lite端侧迁移学习方案只能重新训练预先训练好的模型的最后几层,算是最简单的迁移学习模型,灵活性不足,考虑到端侧的性能和功耗,同时兼顾用户使用体验,是一种适合当前场景的方案。
- 可训练部分为softmax_classifier时,支持交叉熵损失函数,模型支持支持tf lite内置算子。自定义模型的话不支持设置损失函数,模型需ensorflow Select Operators支持。
- 优化器支持典型主流优化器,如SGD、Adam。
- converter,android runtime开源,可被其他应用直接使用,大大降低了第三方开发者开发端侧学习应用门槛。






